Gigabits Over the Legacy Drop

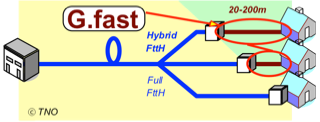
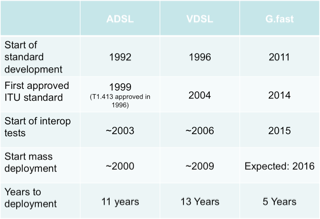
Thanks to a series of three sucessfull CELTIC-NEXT projects, gigabit broadband access to the homes via existing cooper cable is now possible. The projects developed G.fast, a fibre-backhauled broadband access standard able to use the least 20-450 meters of telephony wiring to deliver broadband to homes and businesses without deploying fibre all the way to the homes. G.fast can be seen as DSL system, extending the series of 1) voice band modems 2) ADSL familiy 3) VDSL and now 4) G.fast. Thanks to the three CELTIC-NEXT projects the time of 5 years from standardization to product compared to the previous standard deployments of 13 years can be seen as an outstanding achievement for the time to market of the 4th broadband system generation namely G.fast.
The technical research and development efforts of GOLD can be divided into three key elements:
To increase energy efficiency, a deep sleep/auto wake up functionality is designed and implemented on gateways and sensors. Also, to avoid the high-volume data transfer, a method for model based data compression and reconstruction is developed and implemented.
For reliable sensor to gateway communication in challenging environments, BLE mesh network is developed. This network is based on both non-connectable broadcast advertisement and connection based data transfer. And long-range communication technologies (LoRa and Sigfox) are implemented to determine performance. Also, a simulation software implemented for ad hoc network creation and protocol efficiency measurement.
Remotely configurable gateways are another import outcome of ASUA. A flexible network communication manager is designed and implemented to monitor gateways, process their key parameters and reconfigure them according to a dynamic set of rules. It is based on SNMP protocol. Also, a novel robust communication technique with cloud support developed: Hybrid cloud supported dynamic node addressing and parameter setting.
For server side, standards compliant, scalable ASUA IoT Server is developed.
Cloud technology is one of the key features. It is continuous monitored by adding probes with PRTG and Veeam ONE tools. Resources can be adaptively configured to get a fault tolerant and high available system. Huge observation data are stored on Apache Cassandra, which is a horizontally scalable NoSQL database. Dynamic rule engine, which is remotely configurable, is designed and implemented to generate alarms, notifications, take reconfiguration actions or trigger actuators by evaluating observation data, gateway key parameters or other relevant information sources. ASUA architecture can be seen below.
 One of the most important characteristics of ASUA is standards compliancy. Implemented standards contains but not limited to OGC SOS, MQTT, Open API Specification, GML, OGC WMS, OGC WFS, DSR, AODV, ZigBee, SNMP, IP67, BLE, Wi-Fi, FHIR. In this way, highly interoperable solution is provided to both existing and new systems.
One of the most important characteristics of ASUA is standards compliancy. Implemented standards contains but not limited to OGC SOS, MQTT, Open API Specification, GML, OGC WMS, OGC WFS, DSR, AODV, ZigBee, SNMP, IP67, BLE, Wi-Fi, FHIR. In this way, highly interoperable solution is provided to both existing and new systems.
Totally 10 new products have been developed and 4 products have been improved based on the project results. Partners of the project expect significant return of investment up to 5x.
Further Information:
Web: https://www.celticnext.eu/project-gold/
About GOLD
GOLD project started in January 2015 and finished in December 2017.
The consortium led by Lund University included 14 partners from Sweden, United Kingdom, The Netherlands, Germany, Spain, France, Israel and Belgium which consisted of operstors and suppliers including SME’s, research institutes and universities.
Lund University, Sweden
Nokia Bell N.V., Belgium
ADTRAN GmbH, Germany
Deutsche Telekom AG, Germany
Orange SA, France
SAGEMCOM, France
Sckipio Technologies, Israel
TNO, Netherlands
Marvell Hispania S.L., Spain
Telnet Redes Inteligentes SA, Spain
Ericsson AB (EAB), Sweden
BT (British Telecom), UK
Southampton University, UK
Newcastle University, UK






