Cloud Security with embedded Secure Elements like a SIM Card
Novel solution by Celtic-Plus project SEED4C
Lyon, France. Celtic-Plus project Seed4C has developed a new security concept for the Cloud. The concept is based on a hardware-based solution called “Secure Elements”, which enables more reliable Cloud security.
A major challenge faced by Cloud service providers today is to enable their customers to operate several connected virtual computers running on a shared infrastructure as securely as a physical network of real computers in a private data centre. SEED4C addresses this challenge along with the additional goal that customers should be able to manage and guarantee the security of their virtual computers, as if they were a single entity.
A key aspect of the SEED4C approach is to embed its special security hardware, Secure Elements, in servers to provide trusted security services. This allows securing the cloud applications in a similar way that a SIM card, embedded in a mobile device, allows securing the mobile services. The project was ahead of its time when it was proposed in 2012, when the main trend was to virtualize everything.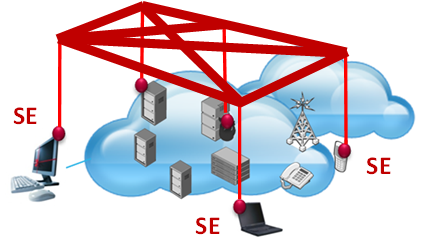
The figure shows the Seed4C approach: the Secure Elements (SEs) are embedded in Cloud nodes and also connected with each other in order to enable the end-to-end enforcement of a security policy and assurance verification. The services offered by this network of SEs provide a way for Cloud customers to manage the security of their virtual machines (VMs) as well as applications and sensitive data handled by these VMs.
Since the start of SEED4C specialised hardware security components for Cloud servers have been developed that can be used to support services such as storage of security keys or the certified location of a server. SEED4C managed to provide a generic way to utilise such components to support a wide range of security and data protection applications in the Cloud.
The basic philosophy of SEED4C is to have the root of trust and security services in hardware components. The project consortium is convinced that this will enhance the security of data in the Cloud. Having trustworthy location information is important for understanding and controlling which regulations apply. This could be a first step in implementing geographical control of data flows, also known as “Schengen Routing”. Other important applications demonstrated by SEED4C were access control in distributed information systems and trustworthy monitoring and logging, e.g. to detect abuses.
The business relevance of the SEED4C project is high. The project presented its results at a moment when trustworthy security is crucial for the uptake of Cloud services. Alcatel-Lucent plans to use SEED4C results to secure the virtualisation of network functions. Many telecoms network operators are considering to implement the solution in their networks. This solution has a high business potential, and the project results have already led to a new product and six improved products.
Download publication as pdf here
About SEED4C:
The SEED4C project ran from April 2012 to December 2014. The consortium, led by Alcatel-Lucent, France, included 21 organisations from 8 countries:
Finland: Nokia, VTT Technical Research Centre of Finland, Cygate, Finceptum Oy, Mikkelin Puhelin Oy
France: Alcatel-Lucent Bell Labs, Gemalto SA, ENS Lyon, INRIA, Wallix
Spain: IKUSI, INNOVALIA, Nextel S.A., VICOMTECH, Software Quality Systems
S-Korea: SOLACIA
For further information, see the project website at: http://www.celticplus-seed4c.org/index.php.






