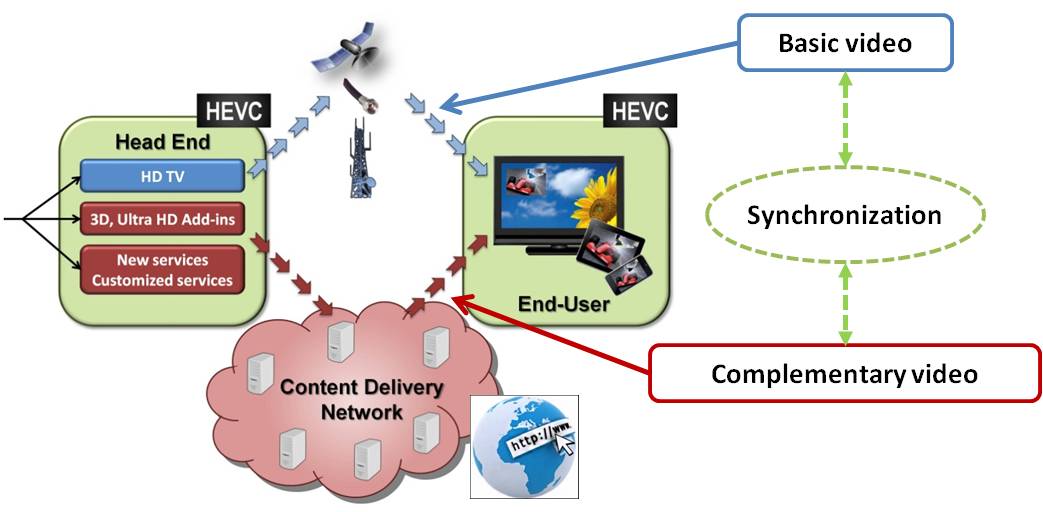
Better video distribution via broadcast and broadband
19 November 2015, Rennes, France: H2B2VS boosts the hybrid broadcast broadband television with innovative use cases and a future-proof synchronization mechanism. An important step in the hybrid distribution of video services was taken by the H2B2VS Celtic-Plus project. Up to now, broadcast and broadband networks were separate worlds in the video consumption business. Some initiatives such as HbbTV (Hybrid Broadcast Broadband TV) have built a bridge between both worlds, but its application is almost limited to provide links over the broadcast channel to content providers’ applications such as catch-up TV services. When it comes to reality, the user is using either one network or the other! H2B2VS allows now to exploit all the potential of real hybrid networks by implementing efficient synchronization mechanisms and using the new video coding standard: High Efficiency Video Coding (HEVC). H2B2Vs hybrid network solution enables value added services with an optimum bandwidth usage in each network with clear commercial applications.
The project followed an end-user oriented approach, studying about twenty use cases and experimenting ten of them.
Several different types of scenarios were addressed by the project.
Picture quality improvement is one of them: 4K pictures can now be displayed by the TV set using a High Definition program broadcast by the terrestrial network and using an enhancement layer sent over the Internet.
The life of handicapped persons can also be improved by H2B2VS technology: Deaf people can receive through the Internet a sign language video of a programme sent over the broadcast channel; the TV set then displays this translation in an inset window.
Other scenarios are addressing the improvement of the Quality of Experience when failures are encountered on a broadcast network: For instance, when experiencing bad satellite receiving conditions, the hybrid receiver automatically and seamlessly switches to the same program streamed over the Internet.
All these scenarios are using the same approach where a basic video is sent over the broadcast network and additional video or data is streamed on the Internet. Both streams are synchronized before being merged and displayed.
Standardization
H2B2VS partners did not stop at developing a technology and test it. They were also very active in standardization: They proposed the so-called “Timed External Media Information” (TEMI) synchronization mechanism to MPEG. TEMI enables to synchronize streams received over different networks with different delays. It is a flexible solution as it offers, according to the use case requirement, different levels of synchronization, up to a frame-accurate one.
MPEG standardized this solution and H2B2VS partners stimulated the adoption of TEMI by DVB (Digital Video Broadcasting) and HbbTV One major outcome of the project is the presence of TEMI in the last release of HbbTV specification (V2.0).
Field trials and demonstrations
Ten use cases were implemented on several demonstrators, reproducing realistic broadcast receiving conditions and making use of an actual broadband network and Content Delivery Network (CDN): A terrestrial demonstrator was setup in France, a satellite one in Spain & Turkey and a cable one in Finland. These trials allowed H2B2VS partners to check that the developed technology was meeting the operational requirements, including specific content protection needs.
The project demonstrated its results on the occasion of several national and international events. The last one was IBC 2015 where H2B2VS partners showcased project’s result on a booth in the “Future Zone” (see the H2B2VS project video).
About H2B2VS:
The H2B2VS project started in January 2013 and completed its work in November 2015.
The consortium, led by Thomson Video Networks, included 14 industrial partners and 6 academics from 5 countries:
- France: Thomson Video Networks, TDF, SmartJog, Civolution, Nagra France, IETR-INSA Rennes, Télécom Paris Tech
- Spain: Alcatel Lucent, Hispasat
- Finland: Teleste, Neusoft Mobile Solutions, VTT Technical Research Centre of Finland, Tampere University of Technology
- Turkey: Vestel, Turk Telekom Argela, Digiturk, Basari Mobile
- Switzerland: Nagravision, École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne, HES-SO
For further information, see the project website at: http://h2b2vs.epfl.ch/